

These individual stock standard solutions were stored in a refrigerator at 4☌ and were used to prepare the working solutions at different concentrations. Stock solutions of 10 000 μg mL −1 of each compound (CIPC, IPC, and 3-CA) were prepared in methanol. ReagentsĬhlorpropham (95%), 3-chloroaniline (99%), and propham (IPC) (99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemi GmbH (Germany) methanol (HPLC grade) was supplied by Fisher Scientific International Company (UK). The main objective of this work was to develop and validate an analytical HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous analysis of CIPC and its metabolite 3-CA using IPC as internal standard. These methods have not included the analysis of CIPC in combination with its degradation products in particular 3-CA. HPLC-UV methods have been used to analyse both CIPC and propham (IPC) in potato products. The internal standard method reported slight improvement of the confidence limit and the relative standard deviation relative to the external standard method. Calibration and quantification were carried out using pure standards of CIPC to achieve good linearity at a concentration range of between 0.01 and 1.5 g/L with a detection limit for CIPC of 0.00039 g/L. The sample injection volume was 10 μL and the detection was set at a wavelength of 240 nm. The chromatographic conditions were set using 60% methanol, at a flow rate of 2 mL/min giving retention times of 4.4 minutes for CIPC and 5.9 minutes for the internal standard. Samples were diluted with methanol containing internal standard of 4-nitrodiphenyl ether. In reviewing the literature, two simple RP-HPLC methods with external and internal standards were developed for the determination of CIPC in emulsifiable concentrates.
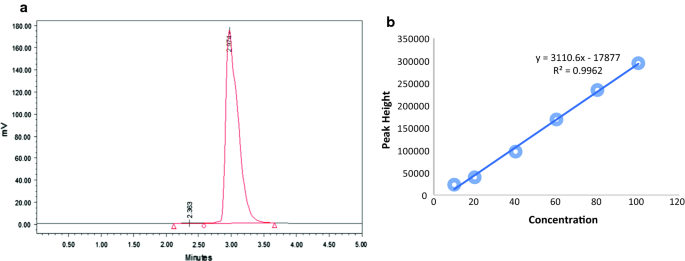
Using HPLC-UV seems to be more appropriate as a final step to analyse phenylcarbamate pesticides. Adequate sensitivity and excellent specificity can be provided by ultraviolet (UV) or electrochemical HPLC detection. However, a lack of a specific, sensitive detector hinders a suitable level of separation for a number of pesticides. HPLC is used to determine carbamate pesticides residues mainly to overcome the thermal liability problems of these pesticides when using gas chromatography (GC). For public health and environmental consideration, there is concern about their residues hence, analytical methods are required to analyse the residues of these phenylcarbamates in potato and environmental samples particularly CIPC and its degradation product 3-chloroaniline 3-CA. CIPC is a compound of the well-known group of N-phenyl carbamates which may undergo rapid degradation under unsuitable solvent and excessive heating conditions releasing 3-CA. Propham (IPC) is a herbicide from the same group as chlorpropham it was applied commercially to prevent sprouting or in combination with chlorpropham, but currently its application is being banned in most countries. IntroductionĬhlorpropham (isopropyl 3-chlorophenyl carbamate) or CIPC is the main sprout inhibitor currently used by potato industry. Despite using the same extract, the recovery results for the proposed HPLC method were 13% higher than GC analysis. The proposed HPLC method was compared with the standard GC method of the CIPC residues extracted showing good agreement. LOD values of CIPC and 3-CA were approximately 0.01 µg/mL whereas the LOQ values were approximately 0.04 µg/mL using repeated injection approach. The method was validated for precision, linearity, the limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ), producing high precision through RSD ≤ 0.03%, and acceptable criteria of the coefficient of determination ( ) of the calibration curves (0.990). The chromatographic conditions required to achieve good separation were 60% mobile phase of methanol, 15-minute run time at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, and a detection wavelength of 210 nm using Phenomenex (ODS-2 250 mm 4.60 mm 5 µm Sphereclone) column at an ambient temperature. An HPLC-UV method was developed and validated for the separation and quantification of these compounds using propham (IPC) as an internal standard. There is concern about the residues of CIPC and its degradation product 3-chloroaniline, 3-CA hence, analytical methods are required to analyse their residues in potato samples. Chlorpropham (CIPC) is the main sprout inhibitor used by potato industry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
